Internet and WWW
A complete notes on Internet and WWW for BCA, BIT and BIM. Topics: internet, application of internet, client server technology, email, video conferencing, ISP, DNS, IP Address, Internet Protocols, Intranet, Extranet, WWW, URL, Browers, Search engine, Web servers, Proxy server, Apache

Internet and WWW
Introduction to Internet:
The internet is a globally connected network system that uses TCP/IP to transmit data via various types of media. The internet is a network of global exchanges including private, public, business, academic and government networks connected by guided, wireless and fiber-optic technologies.
The terms internet and World Wide Web are often used interchangeably, but they are not exactly the same thing; the internet refers to the global communication system, including hardware and infrastructure, while the web is one of the services communicated over the internet.
As computing advanced, peer-to-peer (P2P) communication was gradually delivered and enhanced. Since the 1990s, the internet has greatly influenced and upgraded networking to global standards. Billions of internet users rely on multiple application and networking technologies, including:
Internet Protocol (IP): The internet’s primary component and communications backbone. Because the internet is comprised of hardware and software layers, the IP communication standard is used to address schemes and identify unique connected devices. IP versions used for communications include Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) and Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6).
Communications: The internet is the most cost-effective communications method in the world, in which the following services are instantly available:
- Web-enabled audio/video conferencing services
- Online movies and gaming
- Data transfer/file-sharing, often through File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
- Instant messaging
- Internet forums
- Social networking
- Online shopping
- Financial services
The internet originated with the U.S. government, which began building a computer network in the 1960s known as ARPANET. In 1985, the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) commissioned the development of a university network backbone called NSFNET.
Application of Internet:
Internet can use for different areas some of them are describe below
Business:
In business, the internet can be use for many purposes. An organization can provide details about its products on the internet that can be either used by the other organizations interested in developing business link with it or by the prospective customers.
Marketing:
Now a days internet is used for marketing of the goods and services. Many of the social media like facebook, instagram, youtube etc. which run through internet are becoming great platform for marketing.
Education:
In the field of education the internet is widely used for learning and t4eaching. The internet not only helps the students to search information on various topics of their interest but also provide the platform for e-learning and distance learning. If the website of an educational institution supports e-learning, then the students can participates in online lectures through simulation, web based training (WBT).
Communication:
The people to transfer information to each other use internet. Many services provided by internet such as e-mail, instant massaging help the users to communicate quickly, cheaply, and reliably. We can share knowledge and information with in a second world-wide this is only possible by use of internet.
Entertainment:
The internet is now becoming the great source of entertainment. It provides many entertainment resources like game, movies, songs, photos and many other things.
Government:
These days the internet is playing a crucial role in the functioning of the government organizations. Almost all government organization have set op their websites that provide information related to the organization and people can take government service by home through internet.
Online Shopping:
Now internet is making too easy to do shopping without visiting the shop. We can view the detail about products and can place order and do payment online using online shopping application.
Research:
Internet is one of the best resources for data collection. During research of any topic, we can collect related data from different data warehouse using internet, which make easy and less time consuming as well as within minimum cost.
Connection to the Internet:
To be able to connect to the internet, you need following requirements
- A TCP/IP enabled computer
- Software like web browser
- An account with ISP
- Connection line like telephone line, coaxial cable or fiber optics
- Hardware like Modem or Network Interface Card (NIC) to connect computer to the network of ISP
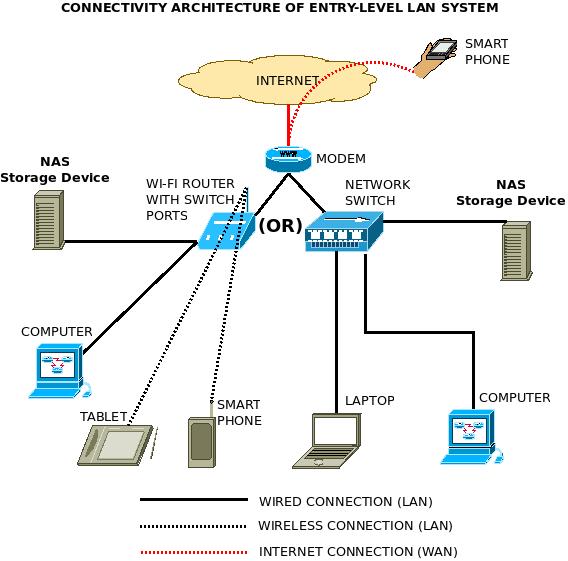
Fig: Internet Connection Setup
Modem-Modulator Demodulator used to translate data from analog to digital and vice versa.
Client-Server Technology:
The Client-server model is a distributed application structure that partitions task or workload between the providers of a resource or service, called servers, and service requesters called clients. In the client-server architecture, when the client computer sends a request for data to the server through the internet, the server accepts the request, process it and deliver the data packets as a response back to the client. Clients do not share any of their resources. Examples of Client-Server Model are Google, Wikipedia, etc.

Fig: Client-Server Architecture
Client: When we talk the word Client, it means to talk of a person or an organization using a particular service. Similarly, in the digital world a Client is a computer (Host) i.e. capable of receiving information or using a particular service from the service providers (Servers).
Servers: Similarly, when we talk the word Servers, It means a person or medium that serves something. Similarly, in this digital world a Server is a remote computer or database, which provides information (data) or particular services.
Email:
Short for electronic mail, e-mail or email is information stored on a computer that is exchange between two users using internet. More plainly, e-mail is a message that may contain text, files, images, or other attachments sent through a network to a specified individual or group of individuals. The first e-mail was sent by Ray Tomlinson in 1971. Tomlinson sent the e-mail to himself as a test e-mail message, containing the text "something like QWERTYUIOP."
An email address consist of two parts separated by @ symbol, the first part is user name and second part is host computer name. the email address look like abcd@gmail.com
Email uses multiple protocols within the TCP/IP suite. For example, SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is used to send messages, while the POP (Post Office Protocol) or IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) protocols are used to retrieve and filter messages from a mail server. When you configure an email account, you must define your email address, password, and the mail servers used to send and receive messages. Fortunately, most webmail services configure your account automatically, so you only need to enter your email address and password. However, if you use an email client like Microsoft Outlook or Apple Mail, you may need to manually configure each account. Besides the email address and password, you may also have to enter the incoming and outgoing mail servers and enter the correct port numbers for each one.
The original email standard only supported plain text messages. Eventually, email evolved to support rich text which supports text formatting, such as bold, italics, and underlining, as well as different fonts, font sizes, and colored text. Rich text documents can also include page formatting options, such as custom page margins, line spacing, and tab widths. Today, email supports HTML, which allows emails to be formatted the same way as websites. HTML email messages can include images, links, and CSS layouts. You can also send files or "email attachments" along with messages. Most mail servers allow you to send multiple attachments with each message, but they limit the total size. In the early days of email, attachments were typically limited to one megabyte, but now many mail servers support email attachments that are 20 megabytes in size or more.
Email was originally written "e-mail," but is now more commonly written as "email" without the dash.
Email Netiquette
Netiquette is short for "Internet etiquette". Just like etiquette is a code of polite behavior in society, netiquette is a code of good behavior on the Internet. This includes several aspects of the Internet, such as email, social media, online chat, web forums, website comments, multiplayer gaming, and other types of online communication.
When composing an email message, it is important to use good netiquette. For example, you should always include a subject that summarizes the topic of the email. It is also helpful to begin each message with the recipient's name and end the message with your name or "signature." A typical signature includes your name, email address, and/or website URL. A professional signature may include your company name and title as well. Most email programs allow you to save multiple signatures, which you can insert at the bottom of an email.
If you want to send an email to multiple recipients, you can simply add each email address to the "To" field. However, if the email is primarily intended for one person, you should place the additional addresses in the "CC" (carbon copy) field. If you are sending an email to multiple people that don't know each other, it is best to use the "Bcc" (blind carbon copy) field. This hides the email addresses of each recipient, which helps prevent spam.
Video Conferencing:
A video conference is a live, visual connection between two or more people residing in separate locations for the purpose of communication. At its simplest, video conferencing provides transmission of static images and text between two locations. At its most sophisticated, it provides transmission of full-motion video images and high-quality audio between multiple locations.
In the business world, desktop video conferencing is a core component of communications applications and web conferencing services, while cloud-based virtual meeting room services enable organizations to deploy video conferencing with minimal infrastructure investment.
Required components of video conferencing systems
The components of a video conferencing system include:
- A network for data transfer, usually a high-speed broadband internet connection, which uses similar technology as voice over Internet protocol (VoIP). Local area network (LAN) and integrated services digital network (ISDN) connections are occasionally used as well
- Two or more video cameras or webcams that provide video input
- Two or more microphones either located on the individual or within the device that provide audio input
- A computer screen, monitor, TV or projector that can broadcast video output
- Headphones, laptop speakers or professional speakers that can be used for audio output
- Hardware or software based coding and decoding technology, called codecs, which can compress analog audio and video (AV) data into digital packets on the distributing end and then decompress the data at the endpoint
- Acoustic echo cancellation (AEC) software which reduces audio delays and supports real time
Types of video conferencing:
- Telepresence Video Conferencing System
Telepresence is designed to host a meeting as closely as possible. Even if the participants are not in the same room physically, the set-up is done in a way easily. Large screens are used and cameras are positioned at eye level. The result is a videoconference set-up that appears as if all the participants are sitting in the same room and around the same table.
- Integrated Video Conferencing System
Integrated video conferencing systems are designed generally for group video conferencing where there's a centralized location for the equipment. It include both the hardware and software. All the main camera, displays and other peripheral videos are mounted in the main conference location. Integrated video conferencing systems are typically ideal for boardroom and classroom conferences.
- Desktop Video Conferencing System
As an important one of types of video conferencing systems, desktop video conferencing system is very popular with people on-the-go and typical office workers. Within this option there are two choices available: a software client on your desktop or a hardware codec that doubles as your computer monitor. By using this type of set-up, the video conferencing system is brought right into your personal computer while still pulling off a full-motion conference.
- Service-based Video Conferencing System
For serviced-based systems, the provider, which often is a telecom carrier, handles majority of the control when it comes to the network set-up. This means less work on your end. You just pay for the solution and your provider manages it for you making more convenient especially if you don't want to bother with the technicalities.
- Codec
This alternative is the most like a room-based video conferencing framework in that it utilizes an outside display, camera and microphone, which is the same as does a framework for your meeting room.
Internet Service Provider (ISP):
An Internet service provider (ISP) is a company that provides customers with Internet access. Data may be transmitted using several technologies, including dial-up (Phone line), DSL (Digital Subscriber line used to transfer digital signal over telephone line), cable modem (A cable modem is a hardware device that allows your computer to communicate with an Internet service provider over a landline connection. It converts an analog signal to a digital signal for the purpose of granting access to broadband Internet), wireless or dedicated high-speed interconnects.
Typically, ISPs also provide their customers with the ability to communicate with one another by providing Internet email accounts, usually with numerous email addresses at the customer’s discretion. Other services, such as telephone and television services, may be provided as well. The services and service combinations may be unique to each ISP. An Internet service provider is also known as an Internet access provider (IAP).
An ISP has the equipment and the telecommunication line access required to have a point-of-presence on the Internet for the geographic area served. The larger ISPs have their own high-speed leased lines so that they are less dependent on the telecommunication providers and can provide better service to their customers. Among the largest national and regional ISPs are AT&T WorldNet, IBM Global Network, MCI, Netcom, UUNet, and PSINet.
Domain Name System (DNS):
Domain Name System is an internet service that translates domain names into IP addresses. Simply the DNS is a TCP/IP application service that converts user-friendly names into IP address. Because domain name is alphabetic, they are easier to remember. When you enter domain name in the browser url then DNS server maps this domain to the corresponding IP address and reached to the correct destination.
For example: the domain name www.example.com might be translated into 192.168.1.10
The last three character of the DNS address indicate the type of the domain.
- Commercial organization as .com
- Educational institutions as .edu
- Governmental organization as .gov
- Network service provider as .net
- Organizations as .org
There are some international domains which assign for different countries as
- Nepal as .np
- Australia as .au
- France as .fr
- Japan as .jp
- United States as .us
- China as .cn
- United Kingdom as .uk
Following figure demonstrates the hierarchy of DNS.
Fig: Hierarchy of DNS
IP Address:
An IP address (internet protocol address) is a numerical representation that uniquely identifies a specific interface on the network.
Addresses in IPv4 are 32-bits long. This allows for a maximum of 4,294,967,296 (232) unique addresses. Addresses in IPv6 are 128-bits, which allow for 3.4 x 1038 (2128) unique addresses.
The total usable address pool of both versions is reduced by various reserved addresses and other considerations.
IP classes
Class A 1 to 127
Class B 128 to 191
Class C 192 to 223
Class D 224 to 239 Reserved for multicast
Class E 240 to 254 Reserved for Future use or research and development
IP addresses are binary numbers but are typically expressed in decimal form (IPv4) or hexadecimal form (IPv6) to make reading and using them easier for humans. In binary notation, IP address if displayed as 32-bits and these 32-bits are represented in 4-octed (8-bites) address or 4-bytes address.
Example: 11000000.10101000.00000001.00000010
To make the IP address more compact and easier to read, IP address are usually written in decimal form with separating each bytes by a dot. Each number in dotted-decimal notation is between 0 and 255.
Example:
192.168.1.2 for IPv4
2001:db8:0:1234:0:578:1:1 for IPv6
Internet Protocols:
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP):
TCP is a popular communication protocol which is used for communicating over a network. It divides any message into series of packets that are sent from source to destination and there it gets reassembled at the destination.
Internet Protocol (IP):
IP is designed explicitly as addressing protocol. It is mostly used with TCP. The IP addresses in packets help in routing them through different nodes in a network until it reaches the destination system. TCP/IP is the most popular protocol connecting the networks.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP):
UDP is a substitute communication protocol to Transmission Control Protocol implemented primarily for creating loss-tolerating and low-latency linking between different applications.
Post office Protocol (POP):
POP3 is designed for allow single user computers to retrieve email from a POP server. The POP server takes email from internet and it look the message and destination email address and store it in the server, later receiver retrieve that mail from the POP server. .
Simple mail transport Protocol (SMTP):
SMTP is designed to send and distribute the e-mail massage between the servers.
Most of the e-mail system that send mail over the internet use SMTP. .
File Transfer Protocol (FTP):
FTP allows users to transfer files from one machine to another. Types of files may include program files, multimedia files, text files, and documents, etc.
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP):
HTTP is designed for transferring a hypertext among two or more systems. HTML tags are used for creating links. These links may be in any form like text or images. HTTP is designed on Client-server principles which allow a client system for establishing a connection with the server machine for making a request. The server acknowledges the request initiated by the client and responds accordingly.
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS):
HTTPS is abbreviated as Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure is a standard protocol to secure the communication among two computers one using the browser and other fetching data from web server. HTTP is used for transferring data between the client browser (request) and the web server (response) in the hypertext format, same in case of HTTPS except that the transferring of data is done in an encrypted format. So it can be said that https thwart hackers from interpretation or modification of data throughout the transfer of packets.
Telnet:
Telnet is a set of rules designed for connecting one system with another. The connecting process here is termed as remote login. The system which requests for connection is the local computer, and the system which accepts the connection is the remote computer.
Gopher:
It is a protocol design to search, retrieve and display documents from remote sites on the internet. It is also possible to initiate online-connections with other system via Gopher. Information accessible via Gopher is stored in Gopher server. These servers do not contain just files but also contains the reference of other servers.
WAIS:
Wide Area Information Server (WAIS) is a client–server text searching system that uses ANSI (American National Standard Institute) Standard Z39.50 Information
Retrieval Service Definition and Protocol Specifications to search index databases on remote computers. WAIS databases contain mostly text-based documents, although WAIS documents may contain sound, pictures or video as well.
Introduction to intranet:
An intranet is a private network that can only be accessed by authorized users. The prefix "intra" means "internal" and therefore implies an intranet is designed for internal communications. "Inter" (as in Internet) means "between" or "among." Since there is only one Internet, the word "Internet" is capitalized. Because many intranets exist around the world, the word "intranet" is lowercase.
The term intranet refers to a network within an organization. Sometimes the term refers only to the organization's internal website, but may be a more extensive part of the organization's information technology infrastructure.
Some intranets are limited to a specific local area network (LAN), while others can be accessed from remote locations over the Internet. Local intranets are generally the most secure since they can only be accessed from within the network. In order to access an intranet over a wide area network (WAN), you typically need to enter login credentials.
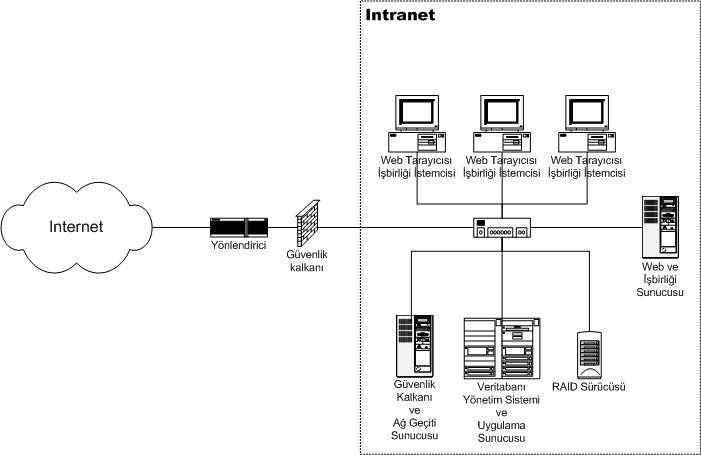
Fig: intranet architecture
Intranets serve many different purposes, but their primary objective is to facilitate internal communication. For example, a business may create an intranet to allow employees to securely share messages and files with each other. It also provides a simple way for system administrators to broadcast messages and roll out updates to all workstations connected to the intranet.
Most intranet solutions provide a web-based interface for users to access. This interface provides information and tools for employees and team members. It may include calendars, project timelines, task lists, confidential files, and a messaging tool for communicating with other users. The intranet website is commonly called a portal and can be accessed using a custom intranet URL. If the intranet is limited to a local network, it will not respond to external requests.
Advantage of Intranet:
Workforce productivity: Intranets can help users to locate and view information faster and use applications relevant to their roles and responsibilities. With the help of a web browser interface, users can access data anytime and from anywhere within the company workstations, increasing employees' ability to perform their jobs faster, more accurately, and with confidence that they have the right information. It also helps to improve the services provided to the users.
Time: Intranets allow organizations to distribute information to employees on an as-needed basis; Employees may link to relevant information at their convenience, rather than being distracted indiscriminately by electronic mail.
Communication: Intranets can serve as powerful tools for communication within an organization, vertically and horizontally. By providing information on the intranet, staff have the opportunity to keep up-to-date with the strategic focus of the organization. Some examples of communication would be chat, email, and or blogs.
Business operations and management: Intranets are also being used as a platform for developing and deploying applications to support business operations and decisions across the internetworked enterprise.
Cost-effective: Users can view information and data via web-browser rather than maintaining physical documents such as procedure manuals, internal phone list and requisition forms. This can potentially save the business money on printing, duplicating documents, and the environment as well as document maintenance overhead. For example, Peoplesoft "derived significant cost savings by shifting HR processes to the intranet".
Enhance collaboration: Information is easily accessible by all authorized users, which enables teamwork.
Immediate updates: When dealing with the public in any capacity, laws, specifications, and parameters can change. Intranets make it possible to provide your audience with "live" changes so they are kept up-to-date.
Disadvantage of intranet:
User Weaknesses: The weakest part of any security system is often its users. When all of your company's computers are connected through an intranet, any compromised machine will give access to shared information on the network. If users rely on easy-to-guess passwords or accidentally download malware or spyware, your entire network could be compromised due to the mistake of one individual. The threat increases if users can access your intranet from home computers or laptops.
Implementation Costs: Building and implementing an intranet network can be expensive. Depending on how many users you need connected and what type of security measures you want to implement, adding an intranet can demand a significant investment.
File Security Risk: While it's true that sharing files and documents between users can boost productivity, it's also true that sharing files puts them at greater risk. When several people as teams are working on documents simultaneously, it's easier for those documents to be potentially be deleted or damaged.
Ongoing Costs: Intranets aren't just costly to implement, they have to be maintained. Costs to consider regarding your intranet include software updates, server upgrades, training of new employees, and consultancy regarding intranet improvements and modifications. A company with an intranet network will also need a full-time IT staff to maintain the network, keep computers connected, and deal with problems as they arise.
Extranet:
An extranet is a network outside the organization or between the two or more organization. It actually combines both the Internet and an intranet. It extends an intranet, or internal network, to other users over the Internet. Most extranets can be accessed via a Web interface using a Web browser. Since secure or confidential information is often accessible within an intranet, extranets typically require authentication for users to access them.
Extranets are often used by companies that need to share selective information with other businesses or individuals. For example, a supplier may use an extranet to provide inventory data to certain clients, while not making the information available to the general public. The extranet may also include a secure means of communication for the company and its clients, such as a support ticket system or Web-based forum.

Fig: Extranet
Advantage of Extranet:
Increased productivity: As you automate processes that were traditionally done manually, bottlenecks will disappear and your company’s productivity will increase. For example, monitor business activities and trigger specific actions, such as automatically placing an order with a supplier when your inventory drops below a certain level.
Flexibility: When you use an extranet to make information and applications available to partners, clients, and customers, everyone can operate when and where it’s most convenient. For example, an extranet may allow you to provide customer-service information outside of regular business hours.
Timely and accurate information: On an extranet you can instantly change, edit, and update sensitive information such as price lists or inventory information.
Reduced inventory: One of the advantage of a business-to-business extranet is its impact on supply-chain management. By linking your inventory system directly to a supplier, you can process orders as soon as the system knows you need them, thus reducing the stock you keep on hand and making order process more efficient.
Build customer loyalty: Extranets make business easier for your customers. The more you make timely, accurate information available to your customers, the more likely it is you’ll keep their business.
Disadvantage of Extranet:
Expensive: Extranets can be expensive to implement and maintain
Security Issues: Security of extranets can be a big concern when dealing with valuable information. System access needs to be carefully controlled to avoid sensitive information falling into the wrong hands.
Create Personal Communication Gap: Extranets can reduce personal contact (face-to-face meetings) with customers and business partners. This could cause a lack of connections made between people and a company, which hurts the business when it comes to loyalty of its business partners and customers.
WWW:
It stands for "World Wide Web". It is important to know that this is not a synonym for the Internet. The World Wide Web, or just "the Web," as ordinary people call it, is a subset of the Internet. The Web consists of pages that can be accessed using a Web browser. The Internet is the actual network of networks where all the information resides. Things like Telnet, FTP, Internet gaming, Internet Relay Chat (IRC), and e-mail are all part of the Internet, but are not part of the World Wide Web.
The World Wide Web is a network of online content that is formatted in HTML and accessed via HTTP. The term refers to all the interlinked HTML pages that can be accessed over the internet. It is technically all the web pages, videos, pictures and other online content that can be accessed via a web browser. The world wide web, or WWW, was first created as a method to navigate the now extensive system of connected computers. It was designed by Tim Berners-Lee through program called Enquire.
Evolution of WWW:
Web 1.0 – The World Wide Web (1990 – 2000)
- Remain limited mostly to static websites
- Mostly publishing / Brochure-ware. Limited to reading only for the majority
- Corporations mostly, no communities
- HTTP, HTML
Web 2.0 – The Social Web (2000 – 2010)
- Publishing as well as Participation
- Social Media, Blogging, Wikis
- Rich User Experience
- Tagging
- Keyword Search
- AJAX, JavaScript Frameworks (jQuery, Dojo, YUI, Ext Js etc), XML,JSON
Web 3.0 – The Semantic Web (2010 – onward)
Semantic means study of meaning in language, programing language, formal logics. Semantic web is a proposed development of the World Wide Web in which, data in web pages is structured and tagged in such a way that it can be read directly by computers.
- Mostly Drag n Drop
- Highly mobile-oriented
- Widgets
- Microblogging
- Cloud Computing
Architecture of Web:
Architecture is divided into several layers as shown in the following diagram:

Fig: Web Architecture
XML=Extensible Markup Language, RDF=Resource Description Framework, RDFS=RDF Scheme, OWL=Web Ontology Language, RIF=Rule Interchange Format, SWRL=Semantic Web Rule Language, SPARQL=Simple Protocol and RDF Query Language
Identifiers and Character Set:
Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) is used to uniquely identify resources on the web and UNICODE makes it possible to built web pages that can be read and write in human languages.
Syntax:
XML (Extensible Markup Language) helps to define common syntax in web.
Data Interchange:
Resource Description Framework (RDF) framework helps in defining core representation of data for web. RDF represents data about resource in graph form.
Taxonomies:
Taxonomy is the science of categorization, or classification, of things based on a predetermined system. In reference to Web sites and portals, a sites taxonomy is the way it organizes its data into categories and subcategories, sometimes displayed in a site map. RDF Schema (RDFS) allows more standardized description of taxonomies and other ontological constructs.
Ontologies:
Ontologies are a formal way to describe taxonomies and classification networks, essentially defining the structure of knowledge for various domains: the nouns representing classes of objects and the verbs representing relations between the objects.
Web Ontology Language (OWL) offers more constructs over RDFS. It comes in following three versions:
- OWL Lite for taxonomies and simple constraints
- OWL DL for full description logic support
- OWL for more syntactic freedom of RDF
Rules
The goal of RIF (Rule Interchange Format) is to define a standard for exchanging rules among rule systems, in particular among Web rule engines.
The Semantic Web Rule Language (SWRL) is a proposed language for the Semantic Web that can be used to express rules as well as logic, combining OWL DL or OWL Lite with a subset of the Rule Markup Language (a subset of Datalog).
RIF and SWRL offers rules beyond the constructs that are available from RDFs and OWL.
Querying
Simple Protocol and RDF Query Language (SPARQL) is SQL like language used for querying RDF data and OWL Ontologies.
Proof
All semantic and rules that are executed at layers below Proof and their result will be used to prove deductions.
Cryptography
Cryptography means such as digital signature for verification of the origin of sources is used.
User Interface and Applications
On the top of layer User interface and Applications layer is built for user interaction.
URL (Uniform Resource Locator):
It is also known as a web address, a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is a standardized naming convention for addressing documents accessible over the Internet and Intranet. An example of a URL is https://www.google.com, which is the URL for the Google website.
http:// or https://
The "http" stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol. It let's the browser to know which protocol it is going to use to access the information specified in the domain. An "https" protocol is short for "Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure" and indicates that information transmitted over HTTP is encrypted and secure. After the http or https is the colon (:) and two forward slashes (//) that separate the protocol from the remainder of the URL.
www.
Next, "www" stands for World Wide Web and is used to distinguish the content. This portion of the URL is not required and many times can be left out. For example, typing "http://webpedia.com" would still get you to the webpedia website.
webpedia.com
Next, "computerhope.com" is the domain name for the website. The last portion of the domain is known as the domain suffix. It is used to identify the type or location of the website. For example, ".com" is short for commercial, ".org" is short for an organization, and ".co.uk" is the United Kingdom. There are dozens of other domain suffixes available. To get a domain, you would register the name through a domain registrar.
/term/
Next, the "term” portions of the above URL are the directory where the web page is located on the server.
computer.html
Finally, computer.html is the actual web page on the domain you're viewing. The trailing .html is the file extension of the web page that indicates the file is an HTML file. Other common file extensions on the Internet include .html, .php,
.xml, .jpg, and .gif. Each of these file extensions performs a different function, like all the different types of files on your computer.
Browsers:
Alternatively referred to as a web browser or Internet browser, a browser is a software program to present and explore content on the World Wide Web. These pieces of content, including pictures, videos, and web pages, are connected using hyperlinks and classified with URLs (Uniform Resource Locators). This page is an example of a web page that can be viewed using a browser.
There have been many different web browsers that have come and gone over the years. The first, named WorldWideWeb (later changed to Nexus), was invented by Tim Berners-Lee in 1990. However, the first graphical browser and widely used browser that help bring popularity to the Internet was NCSA Mosaic.
Some of the popular browsers are:
Google Chrome:
Chrome is a free Internet browser officially released by Google on December 11, 2008. Its features include synchronization with Google services and accounts, tabbed browsing, and automatic translation and spell check of web pages. It also features an integrated address bar/search bar, called the omnibox.
Internet Explorer:
Often abbreviated as IE or MSIE, Microsoft Internet Explorer is an Internet browser that allows users to view web pages on the Internet. Users can also utilize Internet Explorer to listen to and watch streaming content, access online banking, make purchases over the Internet, and much more.
Mozilla Fire Fox:
The Firefox web browser was first released in beta on September 23, 2002, as the "Mozilla Browser," although it was internally code-named "Phoenix." Firefox 1.0 was officially released on November 9, 2004.
Firefox became a popular alternative to Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 when users sought a browser that could better protect them from spyware and malicious websites. As of 2017, it is the fourth-most popular browser after Google Chrome, Apple Safari, and UC Browser.
Opera:
Opera is an Internet browser developed by Opera Software and was first released on April 1, 1995. It is designed for desktops and mobile platforms, including a popular choice for mobile phones. Opera claims to be the fastest browser on earth and has a free e-mail client known as Opera Mail. Some of the popular features of Opera are its speed, tabbed browsing, pop-up control, and voice control.
Apple Safari:
Safari is an Internet browser that was first introduced on June 30, 2003, and is included with Apple macOS and the iPhone. It is also available for iPod Touch and iPad.
Netscape Navigator:
An Internet browser first introduced as Mosaic Netscape 0.9 on October 13, 1994, Netscape was popular during the early 1990s and in a browser war with Microsoft Internet Explorer. The popularity and use of Netscape declined in the late 1990s, which led to the open source Mozilla project and the acquisition on November 24, 1998 by AOL (American Online is a search engine) for $4.2 billion.
As of March 1, 2008, Netscape is no longer supported or used, but old versions can still be downloaded. The picture is an example of what the final version of Netscape Navigator looks like with the Computer Hope web page displayed.
Search Engine:
A search engine is software, usually accessed on the Internet, that searches a database of information according to the user's query. The engine provides a list of results that best match what the user is trying to find. Today, there are many different search engines available on the Internet, each with their own abilities and features. The first search engine ever developed is considered Archie, which was used to search for FTP files and the first text-based search engine is considered Veronica. Currently, the most popular and well-known search engine is Google. Other popular search engines include AOL, Ask.com, Baidu, Bing, and Yahoo.

Fig: Google Search Engine
Web Servers:
A Web server is a computer system that hosts websites. It runs Web server software, such as Apache or Microsoft IIS, which provides access to hosted webpages over the Internet. Most Web servers are connected to the Internet via a high-speed connection, offers faster data transmission rates. A fast Internet connection allows Web servers to support multiple connections at one time without slowing down.
Any computer can be used as a Web server, as long as it is connected to the Internet and has the appropriate software installed. Web servers typically host multiple websites. Some only host a few, while others may host several hundred. Web servers that host websites for multiple users are called "shared hosts." This is the most common type of hosting solution and is used for personal sites, small business sites, and websites run by small organizations. Web servers that only host websites for a single person or company are called "dedicated hosts." These types of servers are appropriate for high-traffic websites and sites that require custom server modifications. Dedicated hosts are also more reliable than shared hosts, since there are fewer sites that can cause bottlenecks or other issues with the server.
How Web Server Works
Web server respond to the client request in either of the following two ways:
- Sending the file to the client associated with the requested URL.
- Generating response by invoking a script and communicating with database
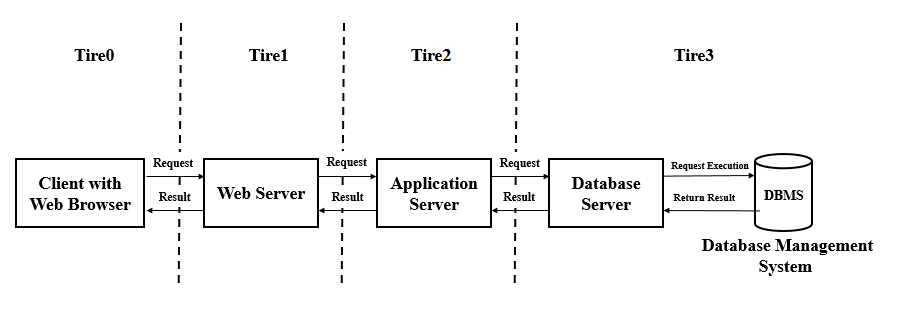
Fig: Web Server Architecture
Key Points
- When client sends request for a web page, the web server search for the requested page if requested page is found then it will send it to client with an HTTP response.
- If the requested web page is not found, web server will the send an HTTP response: Error 404 Not found.
- If client has requested for some other resources then the web server will contact to the application server and data store to construct the HTTP response.
Example of Web Server is:
- Apache Tomcat and Resin
Example of Application Server is:
- JBoss: Open-source server from JBoss community
- Glassfish: Provided by Sun Microsystem. Now acquired by Oracle
- Weblogic: Provided by Oracle. It more secured
- Websphere: Provided by IBM
Apache:
Apache is the most popular Web server software. It enables a computer to host one or more websites that can be accessed over the Internet using a Web browser. The first version of Apache was released in 1995 by the Apache Group. In 1999, the Apache Group became the Apache Software Foundation, a non-profit organization that currently maintains the development of the Apache Web server software.
Apache's popularity in the Web hosting market is largely because it is open source and free to use. Therefore, Web hosting companies can offer Apache-based Web hosting solutions at minimal costs. Other server software, such as Windows Server, requires a commercial license. Apache also supports multiple platforms, including Linux, Windows, and Macintosh operating systems. Since many Linux distributions are also open-source, the Linux/Apache combination has become the most popular Web hosting configuration.
Apache can host static websites, as well as dynamic websites that use server-side scripting languages, such as PHP, Python, or Perl. Support for these and other languages is implemented through modules, or installation packages that are added to the standard Apache installation. Apache also supports other modules, which offer advanced security options, file management tools, and other features. Most Apache installations include a URL rewriting module called "mod_rewrite," which has become a common way for webmasters to create custom URLs.
While the Apache Web server software is commonly referred to as just "Apache", it is technically called "Apache HTTP Server," since the software serves webpages over the HTTP protocol. When Apache is running, its process name is "httpd," which is short for "HTTP daemon."
IIS web server:
Internet Information Services server (IIS server) is a Windows Server-based web application used to deliver website content over the internet to an end user. Internet Information Services is an installable server role, and it is bundled with all Microsoft Windows Server products. More recently, Microsoft has bundled IIS components with the professional versions of their desktop operating system products, such as Windows 10 Pro; however, IIS is typically deployed and centrally managed on one or more Microsoft Windows Servers.
There are two commonly used web server applications available: Apache and Internet Information Services. Apache is an open source installable application commonly used on open system platforms such as Linux, whereas IIS is a server role configured on top of a licensed copy of Windows Server. As IIS is a Microsoft product, IIS offers several advantages over Apache; arguably the biggest advantage is that the user base, in most circumstances, will already be familiar with the product layout, design and terminology, simply because most are existing Windows operators. This makes the product extremely easy to learn and navigate and allows for other Microsoft products to be directly integrated into IIS, such as SharePoint, PowerShell and Microsoft Office.
IIS works through a variety of standard languages and protocols. HTML is used to create elements such as text, buttons, image placements, direct interactions/behaviors and hyperlinks. The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is the basic communication protocol used to exchange information between web servers and users. HTTPS -- HTTP over Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) -- uses Transport Layer Security or SSL to encrypt the communication for added data security. The File Transfer Protocol (FTP), or its secure variant, FTPS, can transfer files.
Proxy Server:
A proxy server acts as a gateway between user and the internet. It’s an intermediary server separating end users from the websites they browse. Proxy servers provide varying levels of functionality, security, and privacy depending on your use case, needs, or company policy.
If you’re using a proxy server, internet traffic flows through the proxy server on its way to the address you requested. The request then comes back through that same proxy server (there are exceptions to this rule), and then the proxy server forwards the data received from the website to you.
Modern proxy servers do much more than forwarding web requests, all in the name of data security and network performance. Proxy servers act as a firewall and web filter, provide shared network connections, and cache data to speed up common requests. A good proxy server keeps users and the internal network protected from the bad stuff that lives out in the wild internet. Lastly, proxy servers can provide a high level of privacy.
How Does a Proxy Server Operate?
Every computer on the internet needs to have a unique Internet Protocol (IP) Address. Just as the post office knows to deliver your mail to your street address, the internet knows how to send the correct data to the correct computer by the IP address.
A proxy server is basically a computer on the internet with its own IP address that your computer knows. When you send a web request, your request goes to the proxy server first. The proxy server then makes your web request on your behalf, collects the response from the web server, and forwards you the web page data so you can see the page in your browser.
When the proxy server forwards your web requests, it can make changes to the data you send and still get you the information that you expect to see. A proxy server can change your IP address, so the web server doesn’t know exactly where you are in the world. It can encrypt your data, so your data is unreadable in transit. And lastly, a proxy server can block access to certain web pages, based on IP address.
Advantage of Proxy Server:
There are several advantages for organizations and individuals to use a proxy server.
To control internet usage of employees and children:
Organizations and parents set up proxy servers to control and monitor how their employees or kids use the internet. Most organizations don’t want you looking at specific websites on company time, and they can configure the proxy server to deny access to specific sites, instead redirecting you with a nice note asking you to refrain from looking at said sites on the company network. They can also monitor and log all web requests, so even though they might not block the site, they know how much time you spend cyberloafing.
Bandwidth savings and improved speeds:
Organizations can also get better overall network performance with a good proxy server. Proxy servers can cache (save a copy of the website locally) popular websites – so when you ask for www.google.com, the proxy server will check to see if it has the most recent copy of the site, and then send you the saved copy. What this means is that when hundreds of people hit www.google.com at the same time from the same proxy server, the proxy server only sends one request to google.com. This saves bandwidth for the company and improves the network performance.
Privacy benefits:
Individuals and organizations alike use proxy servers to browse the internet more privately. Some proxy servers will change the IP address and other identifying information the web request contains. This means the destination server doesn’t know who actually made the original request, which helps keeps your personal information and browsing habits more private.
Improved security:
Proxy servers provide security benefits on top of the privacy benefits. You can configure your proxy server to encrypt your web requests to keep eyes away from reading your transactions. You can also prevent known malware sites from any access through the proxy server. Additionally, organizations can couple their proxy server with a Virtual Private Network (VPN), so remote users always access the internet through the company proxy. A VPN is a direct connection to the company network that companies provide to external or remote users. By using a VPN, the company can control and verify that their users have access to the resources (email, internal data) they need, while also providing a secure connection for the user to protect the company data.
Get access to blocked resources:
Proxy servers allow users to circumvent content restrictions imposed by companies or governments. Some Indian sports channel blacked out online for Nepal. Log into a proxy server on the country where this channel is accessible and watch from there. The proxy server makes it look like you are in India, but you actually live in Nepal. Several governments around the world closely monitor and restrict access to the internet, and proxy servers offer their citizens access to an uncensored internet.